Radon Monitoring and Radon Detection in the Workplace.
This Week is Radon Awareness Week with daily webinars at 10 am highlighting the the risks of Radon and what steps must be taken to minimise the risks. Including Radon Monitoring and Radon Detection in the workplace.
2020 has been a year when lung health has been in the spotlight and “now more than ever we have all become aware of how important it is to look after our lungs” If you have missed any of the webinars they are available https://radonweek.co.uk/
Why is Radon Gas Dangerous?
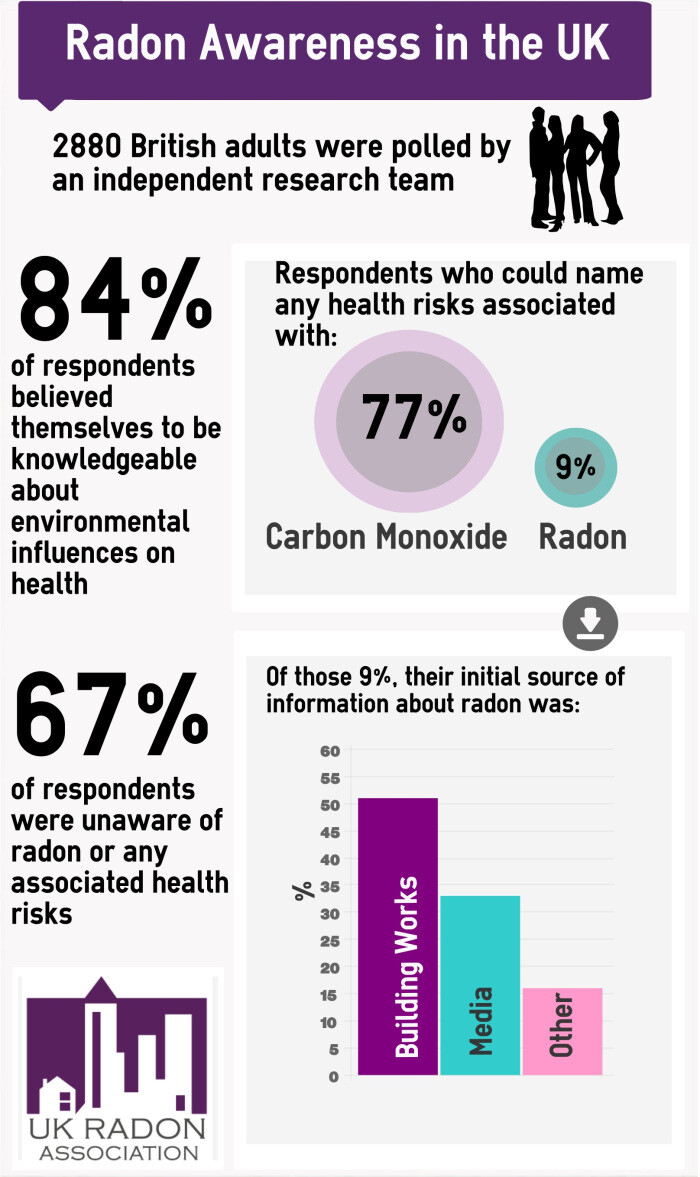
Exposure to radon gas is the leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers and is responsible for over 1100 deaths in the UK every year. High levels of radon can be found in buildings of any type, size or location with occupants unaware of the potential danger unless a specific test has been carried out.
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas and should be considered as indoor air pollution. High levels of radon can cause lung cancer, particularly for smokers and ex-smokers. Radon produces tiny radioactive particles in the air we breathe. Radiation from these particles damages our lung tissue, and over a long period may cause lung cancer. The higher the level and the longer the period of exposure, the greater the risk will be.
The only way to know if a building has a high radon level is to have it tested. If you live or work in a radon affected area we recommend that a test is arranged. All employers are legally obliged to carry out a radon risk assessment. If radon rises into a building it can build up to high concentrations, especially in mines and basements,High concentrations are also found in some buildings because warm air rising draws radon from the ground underneath buildings to enter through cracks and gaps in the floor.But elevated Radon levels can happen in any building.
The Health and Safety at Work 1974 Act sets out the general duties which employers have towards employees and members of the public, and employees have to themselves and to each other. https://www.hse.gov.uk/legislation/hswa.htm
The Ionising Radiations Regulations 2017 https://www.hse.gov.uk/radiation/ionising/legalbase.htm come into effect where radon is present above the defined level of 300 Bq/m3 (as an annual average) and employers are required to take action to restrict resulting exposures. The HSE and Local Authorities are responsible for enforcing these regulations in particular types of workplace.
But if you don’t test you will not know if your building has elevated levels.
When to monitor for radon in the workplace?
Above Ground – if you are located in an “at risk area you should monitor your building
Below ground – For occupied below-ground workplaces (for example those occupied greater than an average of an hour per week or approximately 50 hours per year), or those containing an open water source, the risk assessment should include radon measurements. This applies to all below ground workplaces in the UK (basements, cellars, mines, caves, tunnels, etc), irrespective of the above ground Affected Areas status.
When is a building considered below ground for Radon Monitoring?
This is assessed if there are exterior walls in contact with soil, then those rooms need to be monitored for radon.
For more information on Radon Monitoring and Radon Detection please click here https://www.earthenvironmental.co.uk/radon-monitoring-and-detection/
Earth Environmental & Geotechnical provide a wide range of Radon Monitoring and Detection services click here to contact us for further information.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8acVMO_3Dt0&feature=youtu.be
http://www.radonassociation.co.uk/blog/
https://www.earthenvironmental.co.uk/contact-earth-environmental/